Case Files: Material Failure Notes
NDA-safe examples • simulated micrographs • process diagnostics
Concise case records of metallurgical issues—voids, porosity, cracking—observed in aerospace-grade forging contexts. Entries prioritize mechanism, evidence, and corrective actions.
Metallographic Simulations — Aluminum Alloy
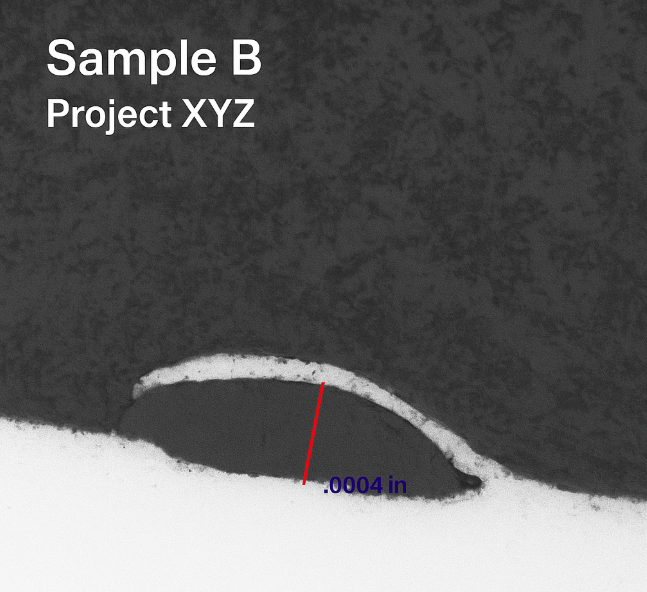
Subsurface Void — Edge Defect
- Material: Aluminum alloy (simulated)
- Inspection: Cross-section, polish, 20× objective
- Dimension: ≈ 0.0004 in
- Likely mechanism: casting/rolling porosity at edge
Edge-localized voids disrupt tool engagement and dimensional control; early detection informs upstream process adjustments.
Hydrogen Porosity — Spherical Void
Typical of moisture-driven entrapment during solidification. Small but impactful on fatigue life for flight-critical parts.

Elongated Gas Void — Collapsed Morphology
Asymmetric collapse intensifies local stress—often a product of rapid cooling or insufficient gas dispersion.

Simulated reference cases — NDA-safe visuals.
Corrosion & Surface Attack — Quick Reference
Pitting — 6261-T6 Aluminum
Cue: isolated elliptical pit with dark rim near boundary transitions.
Cause: chloride ingress + poor passivation + thermal cycling.

Uniform Surface Attack — 304 Stainless
Cue: matte grain etch; even thinning.
Driver: humidity exposure and oxide breakdown.

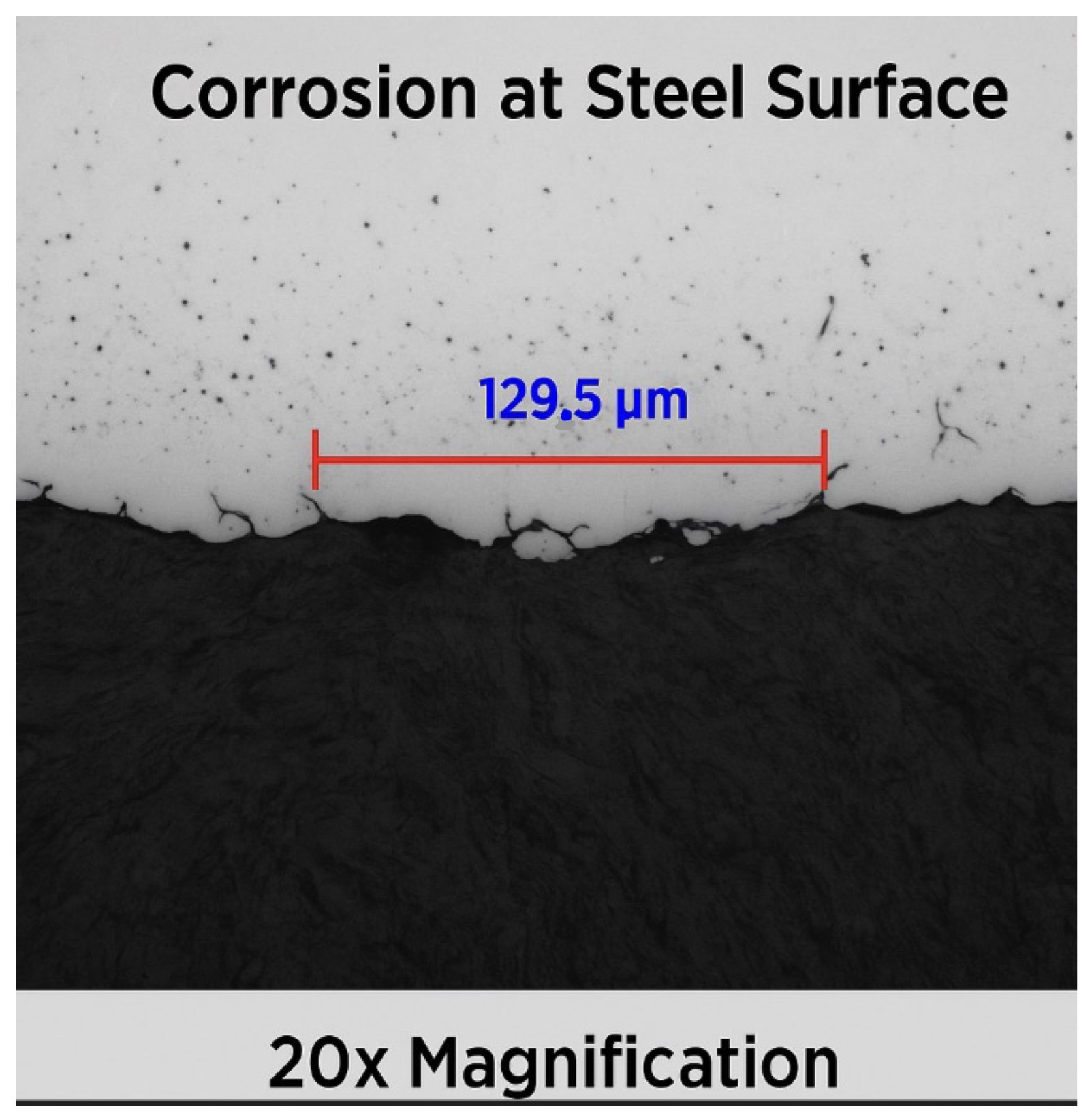
Advanced Trench Attack — Steel Alloy
Jagged, multi-grain loss driven by coating failure + stress + electrolyte pooling.

Galvanic Corrosion — Bimetal Joint
Pair: Aluminum fastener (anodic) + stainless washer (cathodic). Moisture creates an electrolyte bridge; halo forms at the anodic interface.

Hydrogen Embrittlement — High-Strength Steel
Atomic hydrogen ingress + tensile stress → delayed brittle cracking. Common after acid cleaning or plating.

| Material | Mode | Depth / Risk | Visual cue | Primary driver |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 6261-T6 Al | Pitting | 41.2×16.6 µm | Isolated elliptical pit | Cl⁻ ingress + cycling |
| 304 S.S. | Uniform attack | ~54.9 µm | Matte grain etch | Humidity / oxide loss |
| Steel | Trench attack | ~129.5 µm | Jagged trench | Stress + coating failure |
| Al/Stl joint | Galvanic | Variable | Halo at fastener | Potential mismatch |
| HSS | Embrittlement | Crack growth | Brittle subsurface | H uptake + stress |
Alpha Case in Titanium — Notes & Figures
Oxygen-enriched surface layer formed at high temperature. Impact: reduced ductility and fatigue life. Acceptability depends on depth, location, and part criticality.
Fig. 1 — Near-surface alpha case (~2.0 µm)

Fig. 2 — Deeper progression; variable shielding
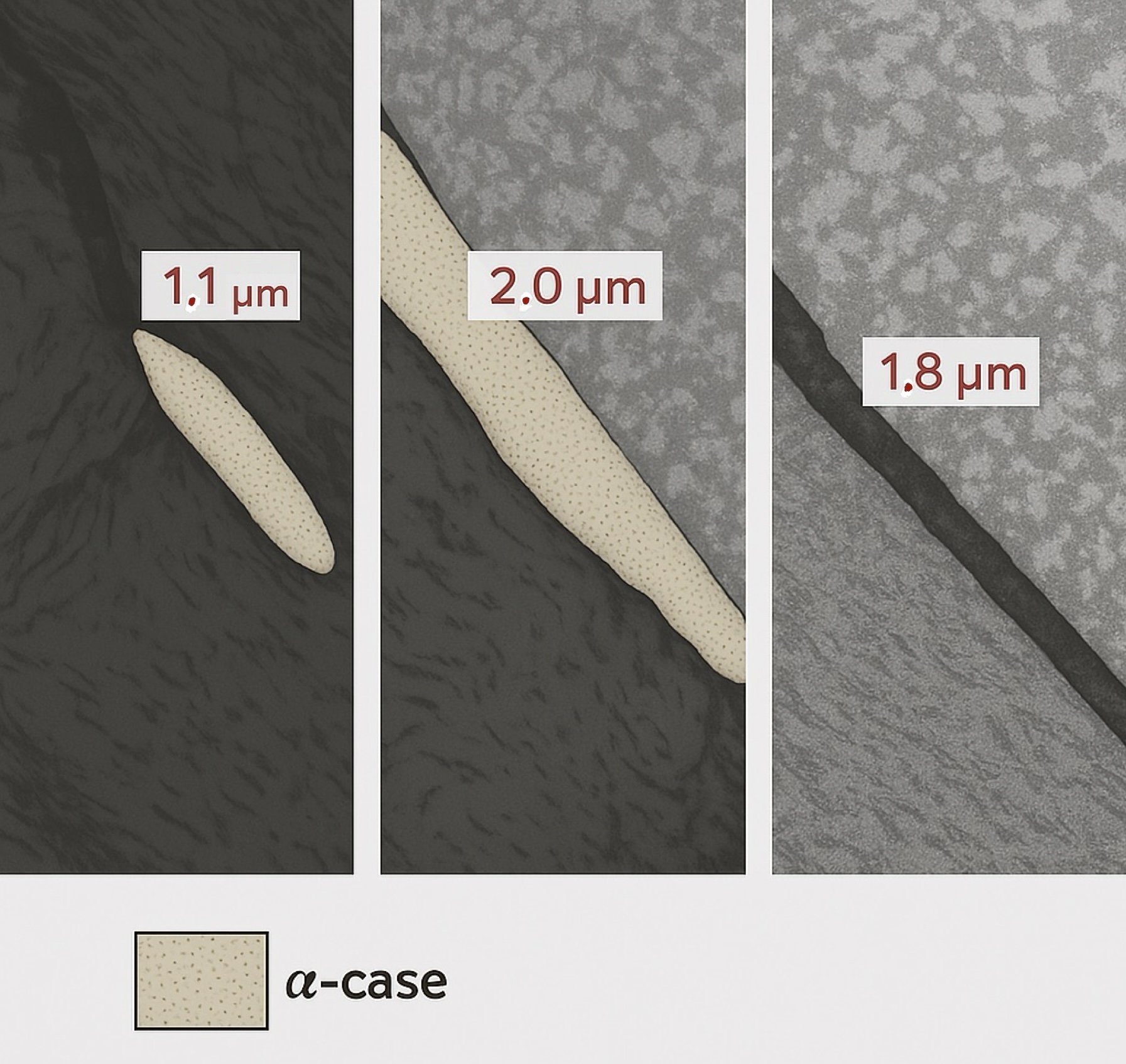
Fig. 3 — Faint rim; controlled condition
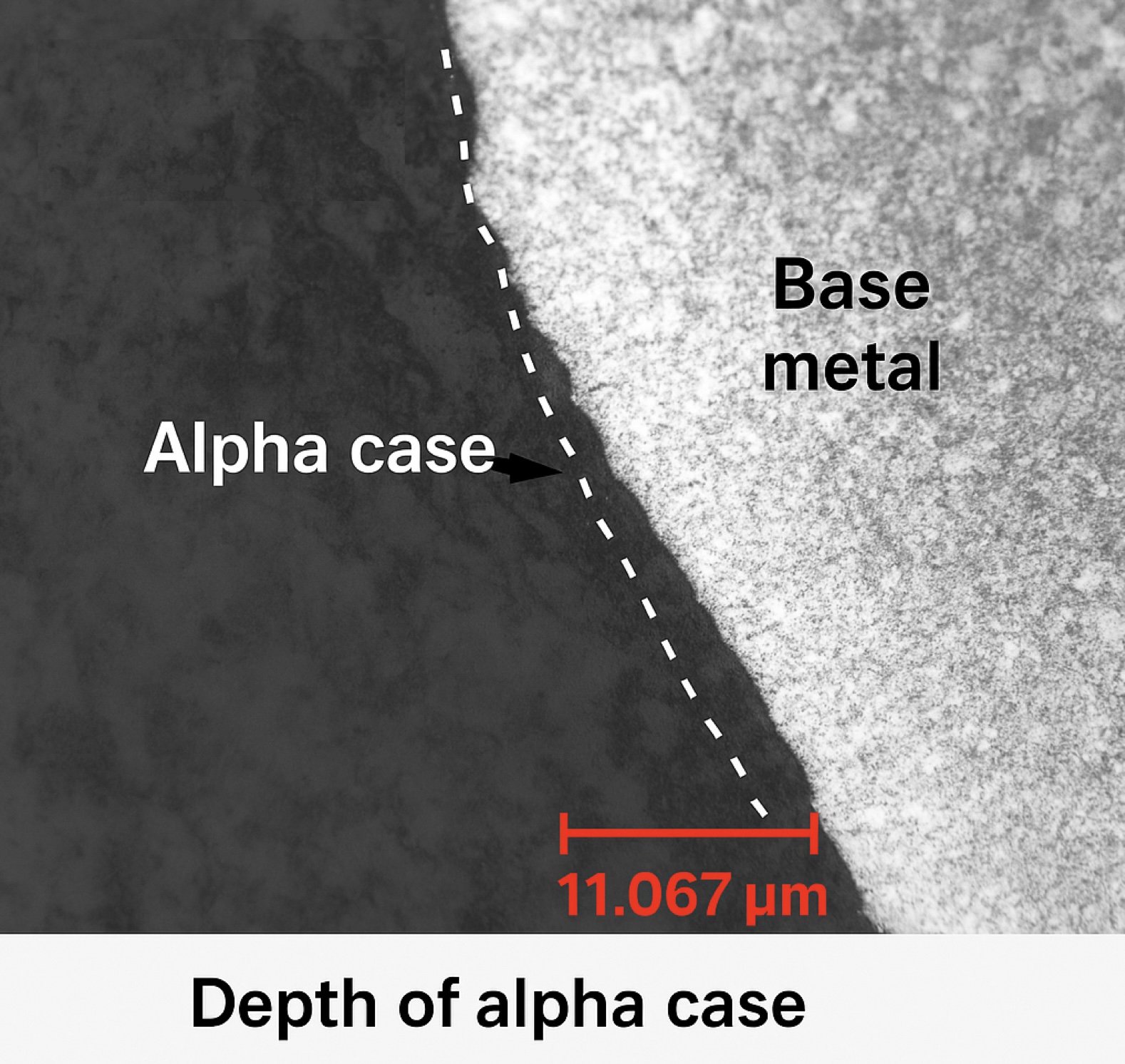
Fig. 4 — Depth variability across surface (1.1–12.6 µm)
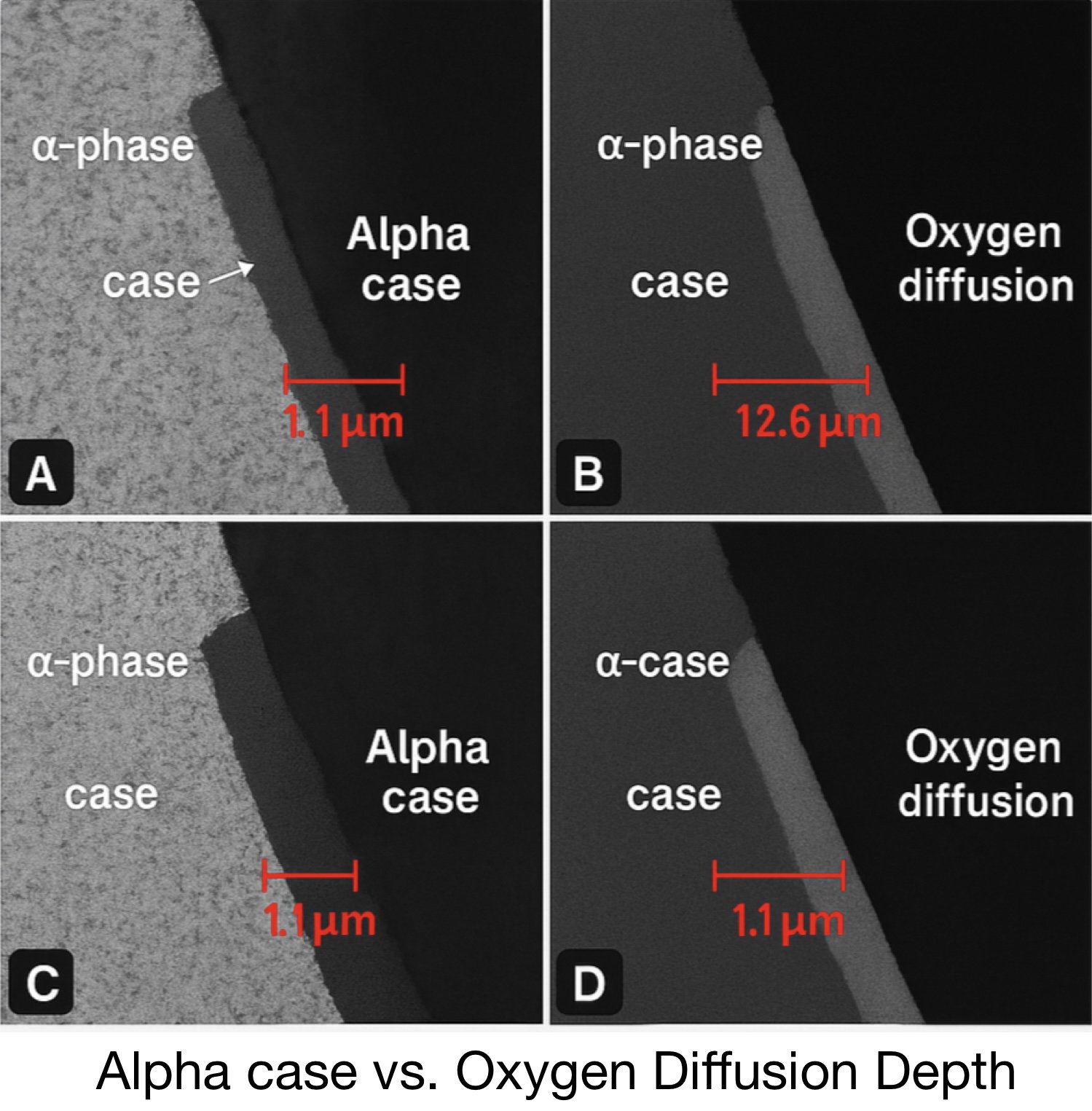
Fig. 5 — Upper limit (~0.002")
