Manufacturing Defects & Failure Modes
Representative microstructural examples used to identify defect morphology, scale, and likely formation mechanisms in forging and high-temperature processing. Focus is on root-cause reasoning and engineering-relevant interpretation.
How I Frame a Case
A repeatable structure for identifying what a defect is, why it forms, and what actions are technically justified.
1) Define
Morphology, location, and scale.
2) Hypothesize
Likely process, material, or environmental drivers.
3) Verify
Targeted checks to confirm or eliminate causes.
4) Mitigate
Controls, rework options, and prevention strategy.

Hydrogen-Induced Subsurface Porosity — Aluminum
Subsurface blister/void morphology consistent with gas porosity that can remain hidden until machining or thermal cycling.
Mechanism
Trapped hydrogen → internal void growth → blistering / breakout risk.
Engineering impact
Fatigue knockdown + late-stage scrap / rework exposure.

Localized Pitting — Aluminum Alloy
Discrete pit morphology used for signature recognition and scale. Often associated with passive film breakdown, inclusions, or aggressive environments.
Mechanism
Passive film breakdown → localized attack → pit growth.
Engineering impact
Stress concentration + crack initiation susceptibility.
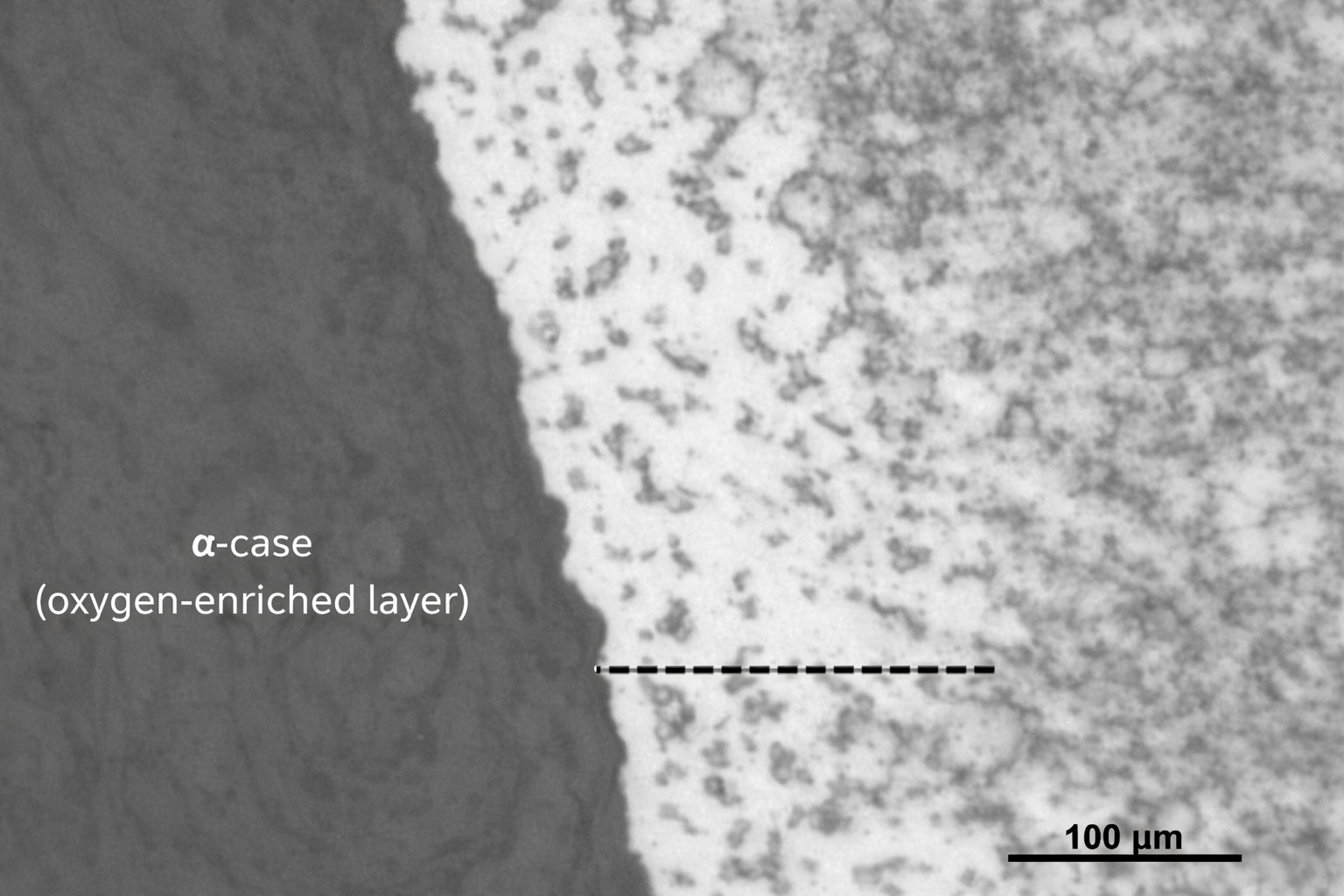
α-Case Formation — Titanium
Oxygen-enriched surface layer formed during high-temperature exposure. A known embrittling condition if not removed post-process.
Mechanism
Oxygen diffusion at temperature → α-stabilized surface zone.
Engineering impact
Embrittlement + fatigue performance risk if retained.

Corrosion Damage — 304 Stainless Steel
Cross-sectional corrosion damage used as a morphology reference for section loss vs. localized pitting signatures.
Mechanism
Localized attack / interface degradation in an aggressive environment.
Engineering impact
Wall thinning + surface integrity and durability concerns.
Images and descriptions are representative examples used for failure-mode recognition and discussion.